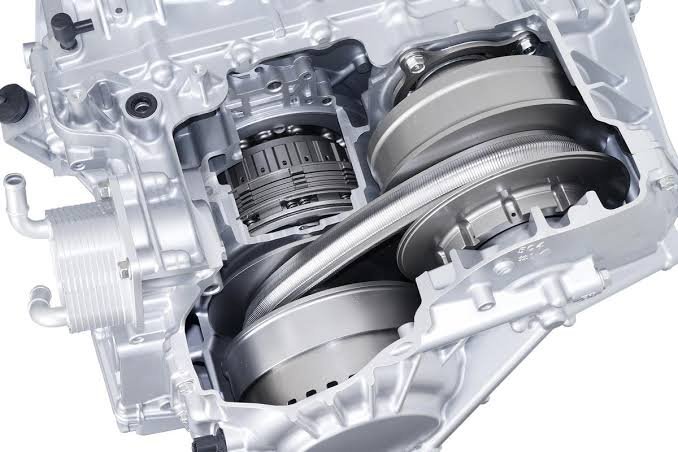
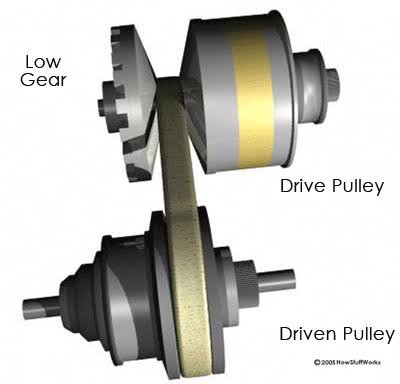
A continuously variable transmission (CVT) is a type of transmission used in vehicles that allows for a nearly infinite number of gear ratios within a certain range, rather than a fixed number of gears like a traditional automatic or manual transmission.
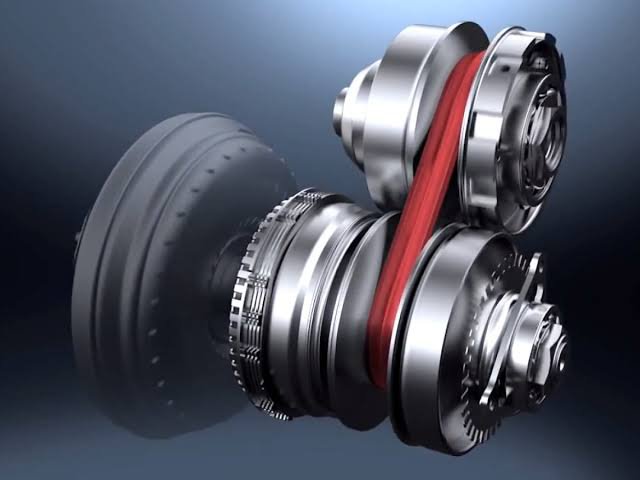
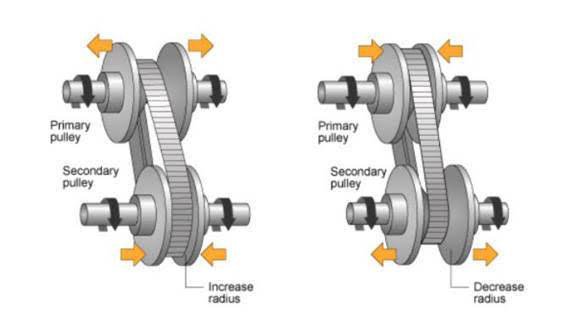
A CVT uses a system of belts or pulleys to transfer power from the engine to the wheels, and the diameter of these components varies depending on the desired gear ratio. This allows the transmission to seamlessly adjust the gear ratio to match the engine’s RPM and the vehicle’s speed, resulting in smoother acceleration and improved fuel efficiency.
CVTs are commonly used in small cars, hybrids, and some SUVs. They have a number of advantages over traditional transmissions, including better fuel efficiency, smoother acceleration, and lower emissions. However, some drivers find the lack of traditional shifting points to be less engaging and less responsive than a traditional automatic or manual transmission. Additionally, some CVTs have been criticized for being noisy or feeling “sluggish” in certain driving situations.


Leave a comment